Pediatrics in Review Care of the Well Newborn Quiz
Bones measurements include length Length Physical growth includes attainment of total acme and appropriate weight and an increment in size of all organs (except lymphatic tissue, which decreases in size). Growth from birth to boyhood... read more , weight Weight Physical growth includes attainment of total summit and appropriate weight and an increase in size of all organs (except lymphatic tissue, which decreases in size). Growth from nativity to boyhood... read more , and head circumference Head Circumference Physical growth includes attainment of full height and advisable weight and an increment in size of all organs (except lymphatic tissue, which decreases in size). Growth from birth to adolescence... read more (encounter likewise Growth Parameters in Neonates Growth Parameters in Neonates Growth parameters and gestational historic period help identify the adventure of neonatal pathology. Growth is influenced past genetic and nutritional factors as well as intrauterine conditions. Growth parameters... read more ). Length is measured from crown to heel; normal values are based on gestational age and should exist plotted on a standard growth chart Physical Growth of Infants and Children Physical growth includes attainment of full superlative and appropriate weight and an increment in size of all organs (except lymphatic tissue, which decreases in size). Growth from birth to boyhood... read more than . When gestational age is uncertain or when the babe seems large for gestational historic period Large-for-Gestational-Age (LGA) Babe Infants whose weight is > the 90th percentile for gestational age are classified as large for gestational age. Macrosomia is birthweight > 4000 g in a term infant. The predominant crusade is... read more or small-scale for gestational age Small-for-Gestational-Age (SGA) Infant Infants whose weight is the 10th percentile for gestational age are classified equally small for gestational historic period. Complications include perinatal asphyxia, meconium aspiration, polycythemia, and... read more than , the gestational age tin can be more precisely determined using physical and neuromuscular findings (see Figure: Assessment of gestational historic period—new Ballard score Cess of gestational age—new Ballard score  ). These methods are typically accurate to ± ii weeks; notwithstanding, in the sick neonate these methods are less reliable.
). These methods are typically accurate to ± ii weeks; notwithstanding, in the sick neonate these methods are less reliable.
Assessment of gestational age—new Ballard score
Scores from neuromuscular and concrete domains are added to obtain total score. (Adapted from Ballard JL, Khoury JC, Wedig K, et al: New Ballard score, expanded to include extremely premature infants. Pediatrics 119(3):417–423, 1991. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82056-six; used with permission of the CV Mosby Company.)
The heart and lungs are evaluated when the babe is tranquillity.
Low-set ears may indicate genetic anomalies Overview of Chromosomal Anomalies Chromosomal anomalies cause various disorders. Anomalies that bear upon autosomes (the 22 paired chromosomes that are alike in males and females) are more common than those that affect sex chromosomes... read more , including trisomy eighteen Trisomy xviii Trisomy 18 is caused past an extra chromosome 18 and is usually associated with intellectual disability, minor nascency size, and various congenital anomalies, including severe microcephaly, center... read more  and trisomy 21 Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Down syndrome is an anomaly of chromosome 21 that tin crusade intellectual disability, microcephaly, short stature, and characteristic facies. Diagnosis is suggested by concrete anomalies and... read more than
and trisomy 21 Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Down syndrome is an anomaly of chromosome 21 that tin crusade intellectual disability, microcephaly, short stature, and characteristic facies. Diagnosis is suggested by concrete anomalies and... read more than 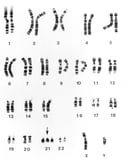 (Down syndrome). Malformed ears, external auditory canals, or both may be present in many genetic syndromes. Clinicians should wait for external ear pits or tags, which are sometimes associated with hearing loss and kidney abnormalities.
(Down syndrome). Malformed ears, external auditory canals, or both may be present in many genetic syndromes. Clinicians should wait for external ear pits or tags, which are sometimes associated with hearing loss and kidney abnormalities.
The splenic border is palpable in about 30% of newborns. Splenomegaly (splenic edge palpable > 2 cm below the left costal margin) suggests congenital infection or hemolytic anemia.
The kidneys may be palpable with deep palpation; the left is more easily palpated than the right. Large kidneys may point obstacle, tumor, or cystic disease.
In boys, the penis should be examined for hypospadias Hypospadias Congenital anomalies of the urethra in boys unremarkably involve anatomic abnormalities of the penis and vice versa. In girls, urethral anomalies may exist without other external genital abnormalities... read more  or epispadias Epispadias Congenital anomalies of the urethra in boys usually involve anatomic abnormalities of the penis and vice versa. In girls, urethral anomalies may exist without other external genital abnormalities... read more
or epispadias Epispadias Congenital anomalies of the urethra in boys usually involve anatomic abnormalities of the penis and vice versa. In girls, urethral anomalies may exist without other external genital abnormalities... read more  . In term boys, the testes should be in the scrotum (see Cryptorchidism Cryptorchidism Cryptorchidism is failure of 1 or both testes to descend into the scrotum; in younger children, information technology is typically accompanied by inguinal hernia. Diagnosis is by testicular test, sometimes... read more than
. In term boys, the testes should be in the scrotum (see Cryptorchidism Cryptorchidism Cryptorchidism is failure of 1 or both testes to descend into the scrotum; in younger children, information technology is typically accompanied by inguinal hernia. Diagnosis is by testicular test, sometimes... read more than  ). Scrotal swelling may signify hydrocele Congenital hydrocele The about common testicular and scrotal anomalies are Built hydrocele Undescended testes (cryptorchidism) Testicular torsion Rare anomalies include scrotal agenesis, hypoplasia, ectopia... read more
). Scrotal swelling may signify hydrocele Congenital hydrocele The about common testicular and scrotal anomalies are Built hydrocele Undescended testes (cryptorchidism) Testicular torsion Rare anomalies include scrotal agenesis, hypoplasia, ectopia... read more 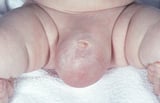 , inguinal hernia Inguinal hernia in neonates Inguinal hernias develop most often in male neonates, especially if they are premature (in which case the incidence is about 10%). The right side is affected most ordinarily, and about x% of... read more , or, more rarely, testicular torsion Testicular Torsion Testicular torsion is an emergency status due to rotation of the testis and consistent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal hurting and swelling, nausea, and vomiting... read more than . With hydrocele, the scrotum transilluminates. Torsion, a surgical emergency, causes ecchymosis and compactness.
, inguinal hernia Inguinal hernia in neonates Inguinal hernias develop most often in male neonates, especially if they are premature (in which case the incidence is about 10%). The right side is affected most ordinarily, and about x% of... read more , or, more rarely, testicular torsion Testicular Torsion Testicular torsion is an emergency status due to rotation of the testis and consistent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal hurting and swelling, nausea, and vomiting... read more than . With hydrocele, the scrotum transilluminates. Torsion, a surgical emergency, causes ecchymosis and compactness.
In term girls, the labia are prominent. Mucoid vaginal and serosanguineous secretions (pseudomenses) are normal; they consequence from exposure to maternal hormones in utero and withdrawal at birth. A small tag of hymenal tissue at the posterior fourchette, believed to be due to maternal hormonal stimulation, is sometimes present only disappears over a few weeks.
Ambiguous genitals (intersex) may indicate several uncommon disorders (eg, congenital adrenal hyperplasia Overview of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a group of genetic disorders, each characterized by inadequate synthesis of cortisol, aldosterone, or both. In the nearly mutual forms, accumulated hormone precursors... read more ; 5-alpha-reductase deficiency; Klinefelter syndrome Klinefelter Syndrome (47,XXY) Klinefelter syndrome is the presence of 2 or more X chromosomes plus one Y, resulting in a phenotypic male person. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings and is confirmed past cytogenetic assay... read more  , Turner syndrome Turner Syndrome In Turner syndrome, girls are born with ane of their 2 10 chromosomes partly or completely missing. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings and is confirmed by cytogenetic analysis. Treatment... read more
, Turner syndrome Turner Syndrome In Turner syndrome, girls are born with ane of their 2 10 chromosomes partly or completely missing. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings and is confirmed by cytogenetic analysis. Treatment... read more  , or Swyer syndrome). Referral to an endocrinologist is indicated for evaluation every bit is a discussion with the family almost benefits and risks of immediate vs delayed sex assignment.
, or Swyer syndrome). Referral to an endocrinologist is indicated for evaluation every bit is a discussion with the family almost benefits and risks of immediate vs delayed sex assignment.
For the Barlow maneuver, the clinician adducts the hip (ie, the knee is fatigued across the body) while pushing the thigh posteriorly. A felt merely not heard clunk indicates that the head of the femur has moved out of the acetabulum; the Ortolani maneuver then relocates it and confirms the diagnosis.
For the Ortolani maneuver, the hip is returned to the starting position; then the hip existence tested is abducted (ie, the genu is moved away from the midline toward the examining table into a frog-leg position) and gently pulled anteriorly. A palpable clunk of the femoral head with abduction signifies movement of an already confused femoral head into the acetabulum and constitutes a positive test for hip dysplasia.
The maneuvers may exist falsely negative in infants > 3 months because of tighter hip muscles and ligaments. If the examination is equivocal or the baby is at high risk (eg, girls who were in the breech position), hip ultrasonography should be washed at 4 to 6 weeks; some experts recommend screening ultrasonography at 4 to six weeks for all infants with risk factors.
The neonate's tone, level of alacrity, motility of extremities, and reflexes are evaluated. Typically, neonatal reflexes, including the Moro, suck, and rooting reflexes, are elicited:
-
Moro reflex: The neonate's response to startle is elicited past pulling the arms slightly off the bed and releasing suddenly. In response, the neonate extends the arms with fingers extended, flexes the hips, and cries.
-
Rooting reflex: Stroking the neonate's cheek or lateral lip prompts the neonate to turn the head toward the impact and open up the mouth.
-
Suck reflex: A pacifier or gloved finger is used to elicit this reflex.
These reflexes are present for several months after nascence and are markers of a normal peripheral nervous system.
A neonate's pare is usually ruddy; cyanosis of fingers and toes is common in the first few hours. Vernix caseosa covers virtually neonates > 24 weeks' gestation. Dryness and peeling often develop inside days, especially at wrist and ankle creases.
Petechiae may occur in areas traumatized during delivery, such as the face when the face is the presenting part; all the same, neonates with diffuse petechiae should exist evaluated for thrombocytopenia.
Many neonates accept erythema toxicum, a benign rash with an erythematous base and a white or yellow papule. This rash, which usually appears 24 hours afterwards birth, is scattered over the trunk and can last for upwards to 2 weeks.
simsaddermild1966.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/care-of-newborns-and-infants/physical-examination-of-the-newborn
Posting Komentar untuk "Pediatrics in Review Care of the Well Newborn Quiz"